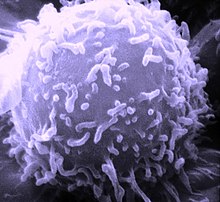
Lymfocyt
Lymfocytter er en type af hvide blodceller.
Der er tre forskellige slags lymfocytter.
B-celler
Den ene af de to lymfocytter kaldes en B-celle eller B-lymfocyt. En B-lymfocyt er et hvidt blodlegeme, som stort set danner antistoffer mod virus og bakterier. Dog er der også nogle af dem der fungerer som hukommelsesceller, hvilket medfører, at den husker tidligere hændelser såsom infektioner og derefter handler hurtigere, hvis den samme form for infektion skulle ramme en igen.
T-celler
Den anden af de to lymfocytter kaldes for en T-celle eller T-lymfocyt. En T-lymfocyt er et hvidt blodlegeme der opretholder immunforsvarets nøgleberedskab. Dens formål er at kunne identificere celler der er blevet ramt af enten et virus eller en bakterie.
NK-celle
Den tredje gruppe er specialiserede lymfocytter, der destruerer kroppens inficerede celler; disse bliver kaldt naturlige dræberceller (NK-celler efter en. Natural Killer).
Indhold i blodet

Eksterne links
- Blodets funktioner og bestanddele. Bloddonorerne i Danmark Arkiveret 19. januar 2012 hos Wayback Machine
| Spire Denne biokemiartikel er en spire som bør udbygges. Du er velkommen til at hjælpe Wikipedia ved at udvide den. |
|
Medier brugt på denne side
Forfatter/Opretter:

- Reusing images
- Conflicts of interest:
None
This diagram shows the hematopoiesis as it occurs in humans. It may look incomplete when rendered directly from WikiMedia. Reference list is found at: File:Hematopoiesis (human) diagram.png
- The morphological characteristics of the hematopoietic cells are shown as seen in a Wright’s stain, May-Giemsa stain or May-Grünwald-Giemsa stain. Alternative names of certain cells are indicated between parentheses.
- Certain cells may have more than one characteristic appearance. In these cases, more than one representation of the same cell has been included.
- Together, the monocyte and the lymphocytes comprise the agranulocytes, as opposed to the granulocytes (basophil, neutrophil and eosinophil) that are produced during granulopoiesis.
- B., N. and E. stand for Basophilic, Neutrophilic and Eosinophilic, respectively – as in Basophilic promyelocyte. For lymphocytes, the T and B are actual designations.
[1] The polychromatic erythrocyte (reticulocyte) at the right shows its characteristic appearance when stained with methylene blue or Azure B.
[2] The erythrocyte at the right is a more accurate representation of its appearance in reality when viewed through a microscope.
[3] Other cells that arise from the monocyte: osteoclast, microglia (central nervous system), Langerhans cell (epidermis), Kupffer cell (liver).
Reference ranges for white blood cells. Values taken from Wikipedia article (Wikipedia:Reference ranges for blood tests). Originally made in Inkscape by Mikael Häggström.
yellow Alpha Helix Section
Electron microscopic image of a single human lymphocyte. Type: Black & White Print