El Niño sydlige oscillation

Rødt = værdier under −7 viser El Niño
Blåt = værdier over +7 viser La Niña
El Niño sydlige oscillation, eng. El Niño Southern Oscillation, forkortet ENSO er en uregelmæssig periodisk variation i vinde, luft- og havoverfladetemperaturer over det tropiske østlige Stillehav, som påvirker klimaet i store dele af troperne og subtroperne. Opvarmningsfasen af havtemperaturen er kendt som El Niño og afkølingsfasen som La Niña. [2]
El Niño er ledsaget af et højt lufttryk i det tropiske vestlige Stillehav og et lavt lufttryk i det østlige Stillehav, og La Niña er lige modsat ledsaget af et lavt lufttryk i det vestlige Stillehav og et lavt lufttryk i det østlige Stillehav. De to faser varer adskillige måneder hver og forekommer typisk med nogle års mellemrum med varierende intensitet pr. periode. [3][4][5]
Henvisninger
- ^ Southern Oscillation Index. Commonwealth of Australia , Bureau of Meteorology
- ^ "El Niño kan påvirke verdensvejret fra sommer og flere år frem. DMI 2023". Arkiveret fra originalen 14. maj 2023. Hentet 14. maj 2023.
- ^ El Niño. Fysikleksikon, Københavns Universitet
- ^ El Niño - Baggrund. ESA, Eduspace 2023
- ^ El Niño og La Niña. Naturgeografi Grundbogen B, Systime
Medier brugt på denne side
ENSO/La Niña state.
- Warm water accumulates in far western Pacific.
- Equatorial water is cooler than in the normal state.
Derived from NOAA / PMEL / TAO diagrams.
http://www.pmel.noaa.gov/tao/proj_over/diagrams/index.htmlForfatter/Opretter: Rainald62, Licens: CC BY-SA 3.0
Southern Oscillation Index monthly data 1876-apr2018, black line:25 months weighted smooth.
Data Source:http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/enso/soi/
Description:http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/glossary/soi.shtml
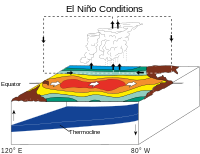
ENSO/El Niño state.
- Sea surface is warm in central and eastern Pacific.
- Less cold water is pulled up along west coast of South America.
- Hot air rises in central Pacific, travels east and west before cooling and descending.
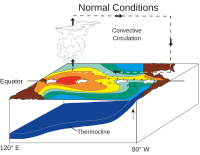
ENSO normal state.
- Normal equatorial winds warm as they flow westward across the Pacific.
- Cold water is pulled up along west coast of South America.
- Warming water is pushed toward west side of Pacific.
- Sea surface is warm in the west.
- Hot air rises in western Pacific, travels eastward and cool air descends on South America.