COVID-19-testning
 Denne artikel bør gennemlæses af en person med fagkendskab for at sikre den faglige korrekthed.
Denne artikel bør gennemlæses af en person med fagkendskab for at sikre den faglige korrekthed.
− bl.a. danske fagudtryk − Desuden kan visse talstørrelser være forældede siden marts/april 2020
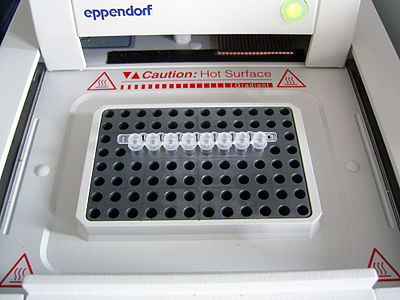
Højre: Eksempel på resultater for en sådan test. Viser for antistofferne IgM og IgG
COVID-19-testning kan identificere SARS-CoV-2-virussen og inkluderer metoder, der både påviser tilstedeværelsen af selve virussen (RT-PCR[note 1]) og metoder, der påviser antistoffer dannet som reaktion på infektion.
Påvisning af antistoffer (jf. serologi, vedr. serum[note 2]) kan bruges både til diagnose og til populationsovervågning. Antistofprøver viser, hvor mange mennesker der har haft sygdommen, inklusive dem, hvis symptomer var mindre eller som var asymptomatiske. En nøjagtig dødelighed af sygdommen og niveauet for flokimmunitet i befolkningen kan bestemmes ud fra resultaterne af denne test. Varigheden og effektiviteten af dette immunrespons er imidlertid stadig uklar.[1]
På grund af begrænset testning havde ingen lande i marts 2020 pålidelige data om forekomsten af virussen i deres befolkning.[2] Per 23. april havde de lande, der offentliggjorde deres testdata, i gennemsnit udført et antal test, der kun svarer til 1,3% af deres befolkning, og intet land havde testet prøver svarende til mere end 13,4% af befolkningen.[3] Der er forskelle i antallet af test, der er udført i de enkelte lande,[4] og denne forskel vil sandsynligvis også påvirke den rapporterede dødelighed, letalitet, 'case fatality rate' '[note 3]), som sandsynligvis er blevet overvurderet i mange lande på grund af bias ved udtagning af stikprøver.[5][6][7]
Galleri
|
|
|
Se også
Noter og referencer
- Noter
- ^ Vedr. RT-PCR : "Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction", polymerasekædereaktion, den kædereaktion der kan opformere genetisk arvemateriale, DNA eller RNA.
- Om "PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)" Arkiveret 25. juni 2020 hos Wayback Machine fra Diagnostik.dtu.dk
- Om isotermiske amplifikationsmetoder (isotermisk nucleinsyre-amplifikation):Jørgen Kjems. "amplificering". Den Store Danske (lex.dk online udgave).
- ^ "Serologi" hos Ordnet.dk
- ^ Om forskellen mellem dødelighed og CFR ('case fatality rate')
- Afsnittet 'Forskel på dødelighed og 'Case Fatality Ratio'-dødelighed' i artiklen "Hvor dødelig er coronavirus?" fra Videnskab.dk 18. marts 2020 af Mike Lee og Sebastian Duchene
- Oversigt over 'case fatality rates' for forskellige sygdomme
- "Tal og overvågning af COVID-19" Arkiveret 29. marts 2020 hos Wayback Machine fra Sst.dk, Sundhedsstyrelsen − Har i tabellen en kolonne med 'Dødsfald i % af smittede ' / 'Case fatality (%)' (en) Arkiveret 3. maj 2020 hos Wayback Machine
- ^ Fra Sundhedsstyrelsen:
* 8. april 2020 : "Information om PCR test for COVID-19 til almen praksis" Arkiveret 28. april 2020 hos Wayback Machine
* 14. april 2020 : (PDF-fil) "Information om PCR test for COVID-19 til almen praksis" Arkiveret 18. april 2020 hos Wayback Machine - ^ Billedbeskrivelse på Commons : "Typical CT imaging manifestation (case 1). A 38 years old male with fever without obvious inducement (39.3 ℃), dry cough and shortness of breath for 3 days. Laboratory test: normal white blood cells (6.35 × 109/L), decreased lymphocytes percentage (4.1%), decreased lymphocytes count (0.31 × 109/L), decreased eosinophil count (0 × 109/L)), increased C-reaction protein (170.91 mg/L), increased procalcitonin (0.45 ng/ml). Imaging examination: multiple patches, grid-like lobule and thickening of interlobular septa, typical "paving stone–like" signs. a SL(Slice): 6 mm; b high-resolution computed tomography(HRCT). HRCT. high-resolution computed tomography"
- ^ Billedbeskrivelse på Commons : "CT imaging of rapid progression stage. A 50 years old female with anorexia, fatigue, muscle soreness, nasal congestion and runny nose for 1 week, sore and itching throat for 2 days. Laboratory test: increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (25 mm/h), normal white blood cells (4.08 × 109/L), decreased lymphocytes (0.96 × 109/ L), increased C-reaction protein (60.8 mg/L). Imaging examination: a (thin layer CT) and b (high-resolution CT) showed multiple patchy and light consolidation in both lungs and grid-like thickness of interlobular septa"
- Referencer
- ^ Abbasi, Jennifer (17. april 2020). "The Promise and Peril of Antibody Testing for COVID-19". JAMA. JAMA Network. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.6170. PMID 32301958. Hentet 20. april 2020. − PubMed: PMID 32301958
- ^ Ioannidis, John P.A. (17. marts 2020). "A fiasco in the making? As the coronavirus pandemic takes hold, we are making decisions without reliable data". STAT. Hentet 22. marts 2020. − Fra Statnews.com
- ^ "Total tests for COVID-19 per 1,000 people". Our World in Data. Hentet 16. april 2020.
- ^ "Iceland has tested more of its population for coronavirus than anywhere else. Here's what it learned". USA Today. 11. april 2020. Hentet 16. april 2020.
- ^ Ward, D. (April 2020) "Sampling Bias: Explaining Wide Variations in COVID-19 Case Fatality Rates". WardEnvironment.
- ^ Henriques, Martha. "Coronavirus: Why death and mortality rates differ". bbc.com (engelsk). Hentet 8. april 2020.
- ^ Michaels, Jonathan A.; Stevenson, Matt D. (2020). "Explaining national differences in the mortality of Covid-19: Individual patient simulation model to investigate the effects of testing policy and other factors on apparent mortality" (PDF). doi:10.1101/2020.04.02.20050633.
Se også
Eksterne henvisninger
 Wikimedia Commons har flere filer relaterede til COVID-19 testing – Coronaviridae
Wikimedia Commons har flere filer relaterede til COVID-19 testing – Coronaviridae- "Instruks for prøvetagning" Arkiveret 23. september 2020 hos Wayback Machine fra Rigshospitalet.dk, afsnit for luftvejssekreter
- "Sådan virker en test for coronavirus - og disse nye testmetoder er på vej" fra Videnskab.dk af Alexander Edwards, lektor ved Biomedical Technology, University of Reading
Om brug af 'POCT' ('point-of-care-testing', diagnogstik nær patienten)
- "Patientsikkerhed ved brug af Point of Care Testing (POCT) og selvtest" (Webside ikke længere tilgængelig) fra Dbio.dk – Oplæring i brug og kvalitetssikring af POCT og selvtestudstyr er et laboratoriefagligt ansvar som skal varetages af bioanalytikere
- WHO's forbehold pr. april 2020 : "Advice on the use of point-of-care immunodiagnostic tests for COVID-19" fra Who.int, 8. april 2020 : "...At present, based on current evidence, WHO recommends the use of these new point-of-care immunodiagnostic tests only in research settings. They should not be used in any other setting, including for clinical decision-making, until evidence supporting use for specific indications is available. ..."
Medier brugt på denne side
Forfatter/Opretter: Partynia, Licens: CC BY-SA 4.0
COVID-19-Test auf Antikörper IgG und IgM
© Raimond Spekking / CC BY-SA 4.0 (via Wikimedia Commons)
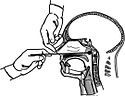
A nasopharyngeal swab being used to test for SARS-CoV-2 virus and the associated COVID-19 illness.
Forfatter/Opretter: Sharafudeen, Calicut Medical College, Licens: CC0
A testing kiosk for covid-19 set up at Government Medical College, Kozhikode
Nasapharyngeal swab
Forfatter/Opretter: Adville, Licens: CC BY-SA 4.0
Ett instrument som analyserar prover för att hitta antikroppar, bland annat för Corona
© Raimond Spekking / CC BY-SA 4.0 (via Wikimedia Commons)
Infektionsschutzzentrum im Kulturquartier/Rautenstrauch-Joest-Museum, Köln. Getestet werden dort ausschließlich Personen, die in sogenannten kritischen Infrastrukturen tätig sind.
Mitarbeiter des Infektionsschutzzentrums demonstrieren an einem Feuerwehrmann, der sich als Testperson zur Verfügung stellt, wie ein Abstrich durchgeführt wird.
Forfatter/Opretter: Adville, Licens: CC BY-SA 4.0
Antibody test IgG and IgM for Corona
CDC 2019-Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Real-Time Reverse Transcriptase (RT)-PCR Diagnostic Panel
Geöffneter Thermocycler mit 8 PCR-Reaktionen
Forfatter/Opretter: Jin, Y., Cai, L., Cheng, Z. et al., Licens: CC BY 4.0
CT imaging of rapid progression stage. A 50 years old female with anorexia, fatigue, muscle soreness, nasal congestion and runny nose for 1 week, sore and itching throat for 2 days. Laboratory test: increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (25 mm/h), normal white blood cells (4.08 × 109/L), decreased lymphocytes (0.96 × 109/ L), increased C-reaction protein (60.8 mg/L). Imaging examination: a (thin layer CT) and b (high-resolution CT) showed multiple patchy and light consolidation in both lungs and grid-like thickness of interlobular septa
Forfatter/Opretter: Jin, Y., Cai, L., Cheng, Z. et al. , for the Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University Novel Coronavirus Management and Research Team, Evidence-Based Medicine Chapter of China International Exchange and Promotive Association for Medical and Health Care (CPAM), Licens: CC BY 4.0
Typical CT imaging manifestation (case 1). A 38 years old male with fever without obvious inducement (39.3 ℃), dry cough and shortness of breath for 3 days. Laboratory test: normal white blood cells (6.35 × 109/L), decreased lymphocytes percentage (4.1%), decreased lymphocytes count (0.31 × 109/L), decreased eosinophil count (0 × 109/L)), increased C-reaction protein (170.91 mg/L), increased procalcitonin (0.45 ng/ml). Imaging examination: multiple patches, grid-like lobule and thickening of interlobular septa, typical "paving stone–like" signs. a SL(Slice): 6 mm; b high-resolution computed tomography(HRCT). HRCT. high-resolution computed tomography



![Nasapharyngeal prøvetagning med vatpind[note 4]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/e/e0/Diagnosis-image1.jpg)

![Typisk CT-skanning[note 5]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/56/COVID19CT2.webp/641px-COVID19CT2.webp.png)
![Hurtigt fremadskridende udviklingstrin ('rapid progression stage'[note 6])](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/8b/COVID19CT1.webp/640px-COVID19CT1.webp.png)