Ozone altitude UV graph
Forfatter/Opretter:
NASA
Kredit:
Shortlink:
kilde:
størrelse:
504 x 380 Pixel (20383 Bytes)
beskrivelse:
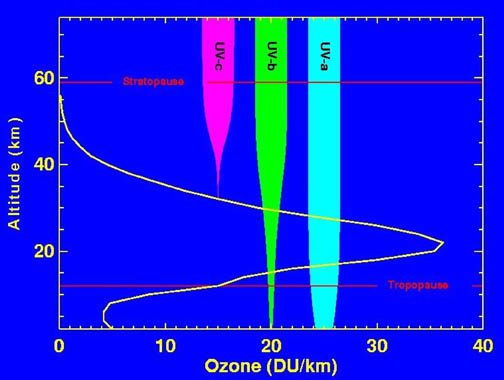
Levels of ozone at various altitudes (DU/km), and related blocking of several types of ultraviolet radiation.
The ozone concentrations shown are very small, typically only a few molecules wide O3 per million molecules of air. But these ozone molecules are vitally important to life because they absorb the biologically harmful ultraviolet radiation from the Sun. There are three different types of ultraviolet (UV) radiation, based on the wavelength of the radiation. These are referred to as UV-a, UV-b, and UV-c. The figure also shows how far into the atmosphere each of these three types of UV radiation penetrates. We see that UV-c (red) is entirely screened out by ozone around 35 km altitude. On the other hand, we see that most UV-a (blue) reaches the surface, but it is not as genetically damaging, so we don't worry about it too much. It is the UV-b (green) radiation that can cause sunburn and that can also cause genetic damage, resulting in things like skin cancer, if exposure to it is prolonged. Ozone screens out most UV-b, but some reaches the surface. Were the ozone layer to decrease, more UV-b radiation would reach the surface, causing increased genetic damage to living things.
Licens:
Public domain
Yderligere oplysninger om licens til billedet kan findes her. Sidste ændring: Tue, 23 Apr 2024 07:07:57 GMT