Conjugation HGT in Bacteria
Forfatter/Opretter:
Attribution:
Billedet er tagget "Attribution Required", men der blev ikke angivet nogen tilskrivningsoplysninger. Attributionsparameteren blev sandsynligvis udeladt ved brug af MediaWiki-skabelonen til CC-BY-licenserne. Forfattere og ophavsmænd finder et eksempel på korrekt brug af eksempel her. her.
Kredit:
Eget arbejde
Shortlink:
kilde:
størrelse:
512 x 571 Pixel (405738 Bytes)
beskrivelse:
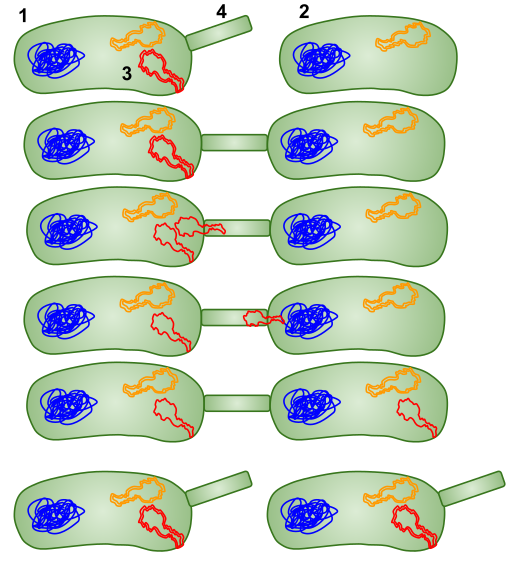
Conjugation occurs when some bacteria have a certain gene on a plasmid that gives them an advantage, and that other bacteria don’t have. This gene usually gives the bacteria an advantage to survive in their environment, usually when the environment has antibiotics in it. A bacteria with the antibiotic resistant gene (the donor bacteria) finds a bacteria without this gene and attaches a sex pilus to it. The plasmid that gives the advantage is a double helix, which then the helixes are separated, and one strand (called T-DNA) is sent through the pilus to the other bacteria. The T-DNA in both bacteria are then replicated to become double helixes. Both bacteria can now give this plasmid with other bacteria through sex pili.
Licens:
Licensbetingelser:
Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0
Yderligere oplysninger om licens til billedet kan findes her. Sidste ændring: Mon, 07 Oct 2024 22:59:26 GMT